Enable SNMP Traps
Description
SNMP traps are information sent using the SNMP protocol from monitored resources to a poller server. This information contains multiple attributes, including:
- Address of the resource sending the information.
- The root OID (Object Identifier) corresponding to the identifier of the message received.
- The message sent via the SNMP trap which corresponds to a set of settings (1 to N).
In order to be able to interpret the event received, the Network supervisor server needs to possess in its configuration the necessary elements to translate the event. For this, it must have a database containing the OID and the descriptions, known as MIB files. There are two types of MIB:
- Standard MIBs that use standardized OIDs and are implemented by numerous manufacturers on their equipment.
- MIB manufacturers who are specific to each one and often to each equipment model.
MIB manufacturers can be retrieved from the equipment. Centreon allows us to store the definition of SNMP traps in its MariaDB/MySQL database. The traps can subsequently be linked to passive services via the Relations tab of the definition of a service.
Architecture
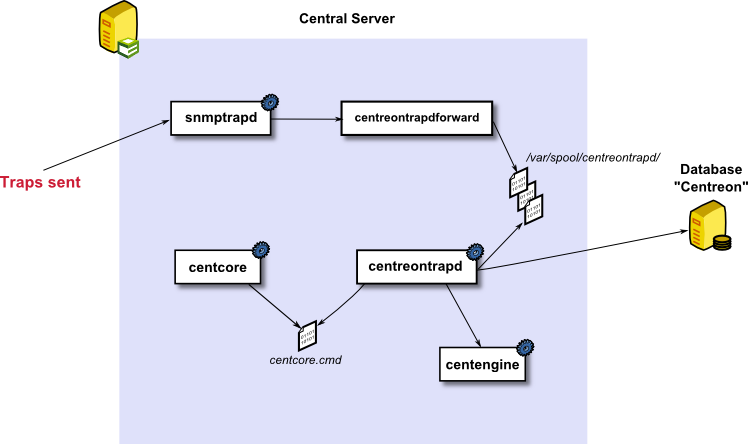
SNMP trap processing by the central server
The processing of an SNMP trap is as follows:
- snmptrapd is the service enabling the retrieval of SNMP traps sent by the equipment (by default it listens on port UDP 162).
- Once the SNMP trap has been received, it is sent to the ‘centreontrapdforward’ script, which writes the information received in a buffer folder (by default /var/spool/centreontrapd/).
- The ‘centreontrapd’ service reads the information received in the buffer folder and interprets the traps received, checking, in the centreon database, the actions necessary to process these events.
- The ‘centreontrapd’ service transmits the information to the scheduler or the ‘gorgoned’ service (to send the information to a remote scheduler), which changes the status and the information associated with the service to which the SNMP trap is linked.
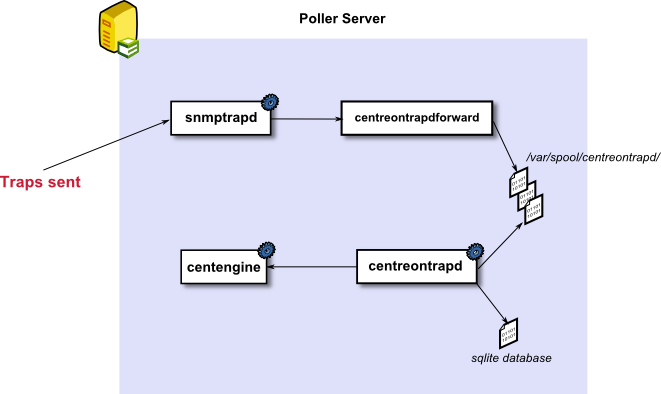
SNMP trap processing by a poller server
To keep a copy of the configuration of the SNMP traps on each satellite server, an SQLite database is charged with keeping the information of the traps contained in the MariaDB/MySQL database cached. This SQLite database is automatically generated by the central server.
The processing of an SNMP trap is as follows:
- snmptrapd is the service used to retrieve the SNMP traps sent by the equipment (by default it listens on port UDP 162).
- Once the SNMP trap has been received, it is sent to the ‘centreontrapdforward’ script, which writes the information received in a buffer folder (by default /var/spool/centreontrapd/).
- The ‘centreontrapd’ service reads the information received in the buffer folder and interprets the various traps received, checking in the SQLite database for the actions to be taken to process the traps received.
- The ‘centreontrapd’ service transmits the information to the scheduler, which changes the status and the information associated with the service to which the SNMP trap is linked.
The Centreon Gorgone process is responsible for copying the SQLite base on the remote poller.
Successive actions by the centreontrapd process
Successive actions by the centreontrapd process are:
Configuring services
Snmptrapd
To call the ‘centreontrapdfoward’ script, the file /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf must contain the following lines:
disableAuthorization yes
traphandle default su -l centreon -c "/usr/share/centreon/bin/centreontrapdforward"
You can optimize the performance of snmptrapd by using the following options:
- -On don’t try to convert the OIDs
- -t don’t log the traps to the syslog server
- -n don’t try to convert the IP addresses into host names
These options can be changed in the file /etc/sysconfig/snmptrapd:
OPTIONS="-On -d -t -n -p /var/run/snmptrapd.pid"
centreontrapdforward
To change the buffer folder to which the information will be written, change the configuration file /etc/centreon/centreontrapd.pm:
our %centreontrapd_config = (
spool_directory => '/var/spool/centreontrapd/',
);
1;
You can also map the folder in the RAM, by adding the following line in the file /etc/fstab:
tmpfs /var/spool/centreontrapd tmpfs defaults,size=512m 0 0
centreontrapd
Two configuration files exist in centreontrapd:
- /etc/centreon/conf.pm contains the connection information to the MariaDB/MySQL database
- /etc/centreon/centreontrapd.pm contains the configuration of the centreontrapd service
Configuration of the service
In the file /etc/centreon/centreontrapd.pm we advise changing three settings only (if necessary):
- If the mode option is defined in 1 centreontrapd functions on a satellite server, otherwise it functions on a central server (centreon).
- The centreon_user option can be used to change the user executing the actions.
- The spool_directory option can be used to change the buffer folder to be read (if you have changed it in the ‘centreontrapdforward’ configuration file).
Here is an example of possible configuration of the file /etc/centreon/centreontrapd.pm (the configuration file can be changed with ‘-config-extra = xxx’):
our %centreontrapd_config = (
# Time in seconds before killing not gently sub process
timeout_end => 30,
spool_directory => "/var/spool/centreontrapd/",
# Delay between spool directory check new files
sleep => 2,
# 1 = use the time that the trap was processed by centreontrapdforward
use_trap_time => 1,
net_snmp_perl_enable => 1,
mibs_environment => '',
remove_backslash_from_quotes => 1,
dns_enable => 0,
# Separator for arguments substitution
separator => ' ',
strip_domain => 0,
strip_domain_list => [],
duplicate_trap_window => 1,
date_format => "",
time_format => "",
date_time_format => "",
# Time in seconds before cache reload
cache_unknown_traps_retention => 600,
# 0 = central, 1 = poller
mode => 0,
cmd_timeout => 10,
centreon_user => "centreon",
# 0 => skip if MariaDB error | 1 => don't skip (block) if MariaDB error (and keep order)
policy_trap => 1,
# Log DB
log_trap_db => 0,
log_transaction_request_max => 500,
log_transaction_timeout => 10,
log_purge_time => 600
);
1;
Configuring the database connection
On Centreon Central server, edit the /etc/centreon/conf.pm file:
$centreon_config = {
VarLib => "/var/lib/centreon",
CentreonDir => "/usr/share/centreon/",
"centreon_db" => "centreon",
"centstorage_db" => "centreon_storage",
"db_host" => "localhost:3306",
"db_user" => "centreon",
"db_passwd" => "centreon"
};
1;
On a poller, edit the /etc/centreon/centreontrapd.pm file:
our %centreontrapd_config = (
...
"centreon_db" => "dbname=/etc/snmp/centreon_traps/centreontrapd.sdb",
"centstorage_db" => "dbname=/etc/snmp/centreon_traps/centreontrapd.sdb",
"db_host" => "",
"db_user" => "",
"db_passwd" => "",
"db_type" => 'SQLite',
...
);
1;