Commands
Definition
A command is the definition of a line of command which uses a script or an application to perform an action. It is possible to execute this command by specifying arguments.
There are four types of command:
- Verification commands are used by the schedulers to verify the status of a host or of a service.
- Notification commands are used by the schedulers to alert the contacts (via mail, SMS, etc.).
- Discovery commands are used by the schedulers to discover.
- Miscellaneous commands are used by the additional modules (to perform certain actions), by the scheduler for data processing, etc.
All the commands can be configured in the menu: Configuration > Commands.
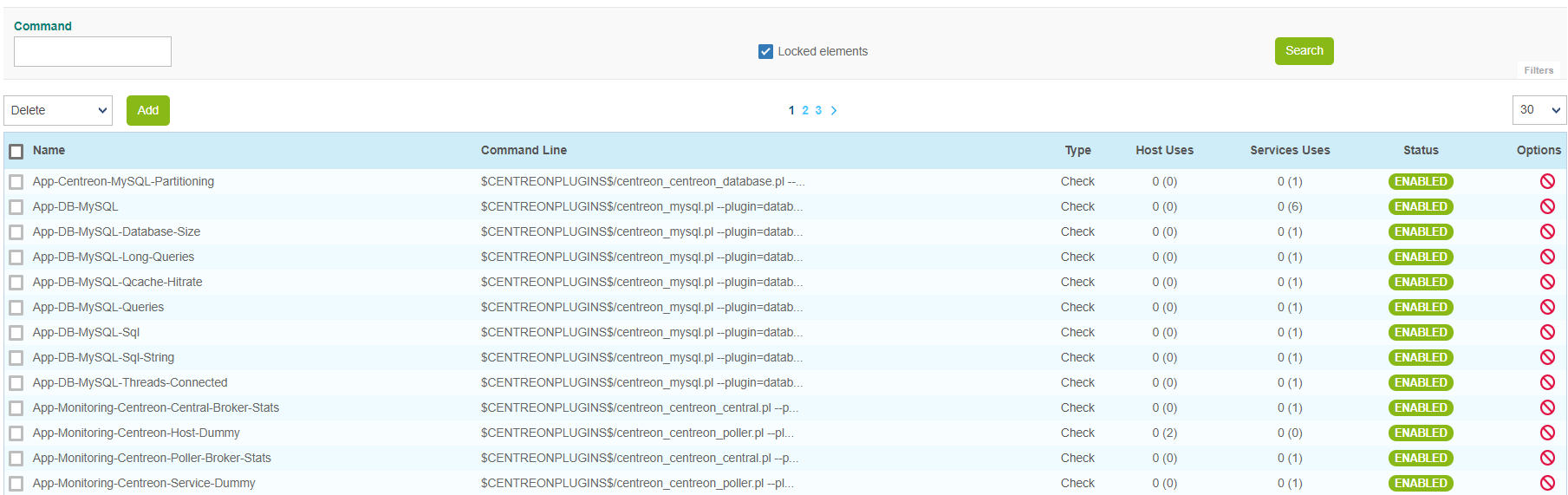
By default, locked commands are hidden. Check the "Locked elements" box to list all commands.
Adding a command
- Go to the Configuration > Commands menu
- Click on Add
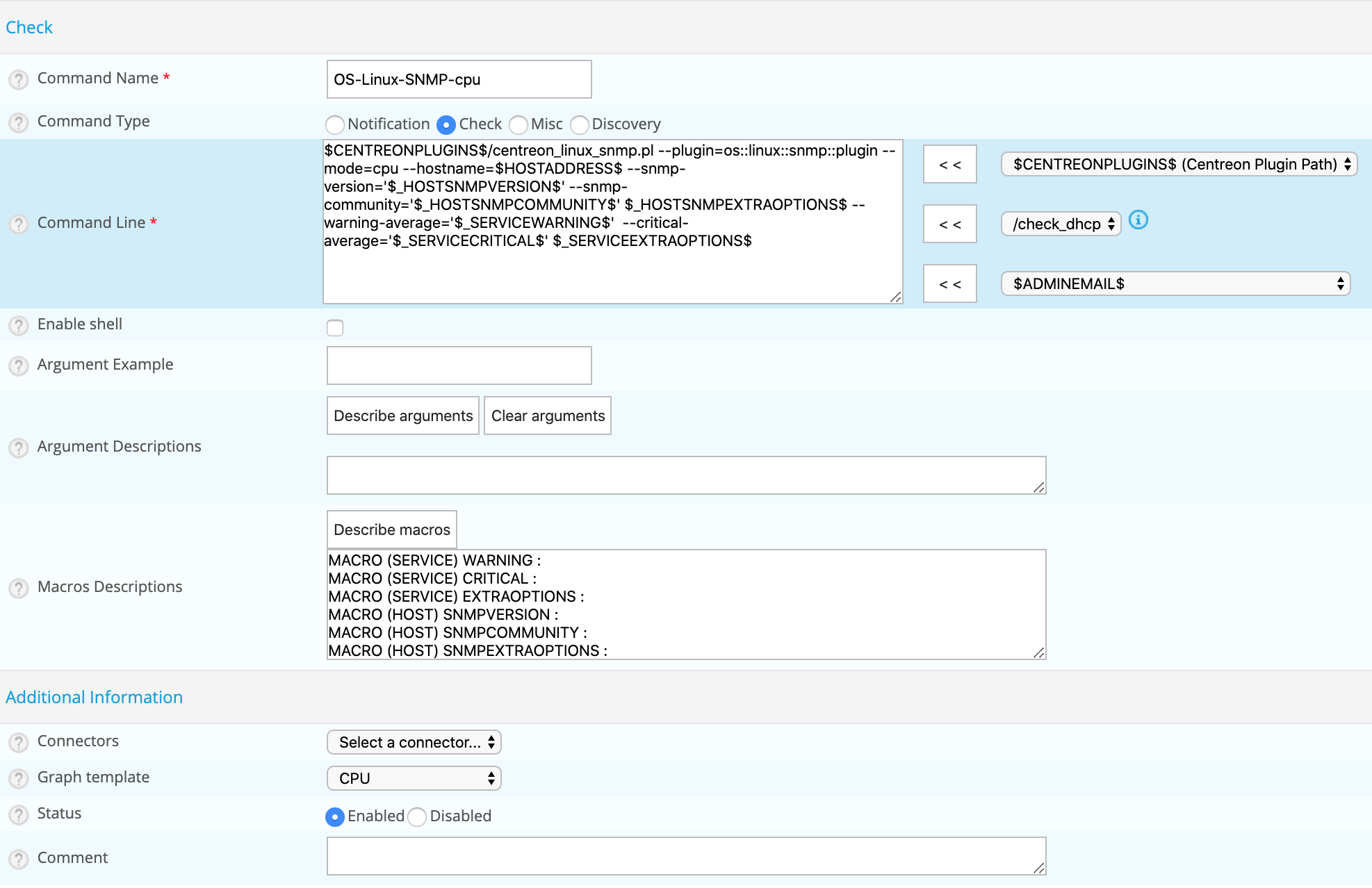
The configuration fields of a command are the same regardless of the type of command chosen.
Configuration fields
- The command Name field defined the name of the command.
- The Command Type field allows us to choose the type of command.
- The Command Line field indicates the application or the script use with the command.
- The Enable shell box allows us to enable functions that are specific to a shell such as the pipe, etc.
- The Argument Example field define examples of arguments (each argument starts with a ”!”)
- The Describe arguments button serves to add a description to arguments of the “$ARGn$” type. This description will be visible when using the command in a host or service form.
- The Clear arguments button deletes the description of arguments defined
- The Describe macros button serves to add a description to all macros. This description will be visible when using the command in a host or service form.
- The Connectors selectlist serves to link a Connector to the command. For more information on Connectors refer to the chapter entitled Perl Connector and SSH Connector.
- The Graph template field serves to link the command to a graphic model.
- The Comment field can be used to make a comment on the command.
Arguments and macros
In the Command Line field it is possible to use macros and arguments.
The macros are used to be able to pass various settings to the scripts called up by the commands. During execution of the command by the scheduler, each of the arguments and macros are replaced by their respective values. Each macro appears in the form $value$:
$CENTREONPLUGINS$/centreon_linux_snmp.pl --plugin=os::linux::snmp::plugin --mode=cpu \
--hostname=$HOSTADDRESS$ --snmp-version='$_HOSTSNMPVERSION$' \
--snmp-community='$_HOSTSNMPCOMMUNITY$' $_HOSTSNMPEXTRAOPTIONS$ \
--warning-average='$_SERVICEWARNING$' \
--critical-average='$_SERVICECRITICAL$' $_SERVICEEXTRAOPTIONS$
Good practice requires replacing the arguments by custom macros.
Connectors
SSH connector
Centreon SSH Connector is a free software from Centreon available under the Apache Software License version 2 (ASL 2.0). It speeds up execution checks over SSH when used along Centreon Engine.
Installation
Centreon recommends using its official packages. Most of Centreon’ endorsed software are available as RPM packages.
Run the following commands as privileged user:
yum install centreon-connector-ssh
Or you can build the Centreon SSH Connector. You will need the following external dependencies:
- a C++ compilation environment.
- CMake (>= 2.8), a cross-platform build system.
- Centreon Clib, The centreon Core library.
- ssh2 library to use ssh functions.
- gcrypt library to secure connections.
This program is compatible only with Unix-like platforms (Linux, FreeBSD, Solaris, ...).
Prerequisites
- CentOS
- Debian/Ubuntu
- OpenSUSE
In CentOS you need to add manually cmake. After that you can install binary packages. Either use the Package Manager or the yum tool to install them. You should check packages version when necessary.
Package required to build:
| Software | Package Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C++ compilation environment | gcc gcc-c++ make | Mandatory tools to compile. |
| CMake (>= 2.8) | cmake | Read the build script and prepare sources for compilation. |
| Centreon Clib (>= 1.0) | centreon-clib-devel | Core library used by Centreon Connector. |
| ssh2 library | libssh2-devel | SSH library. |
| gcrypt library | libgcrypt-devel | Gcrypt library. |
- Install basic compilation tools
yum install gcc gcc-c++ make libssh2-devel libgcrypt-devel
- Install cmake
yum install cmake
- Install Centreon Clib
See the Centreon Clib @TODO@:ref:documentation <centreon-clib:centreon_clib_install>.
In recent Debian/Ubuntu versions, necessary software is available as binary packages from distribution repositories. Either use the Package Manager or the apt-get tool to install them. You should check packages version when necessary.
Package required to build:
| Software | Package Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C++ compilation environment | build-essential | Mandatory tools to compile. |
| CMake (>= 2.8) | cmake | Read the build script and prepare sources for compilation. |
| Centreon Clib (>= 1.0) | centreon-clib-devel | Core library used by Centreon Connector. |
| ssh2 library | libssh2-1-dev | SSH library. |
| gcrypt library | libgcrypt11-dev | Gcrypt library. |
- Install compilation tools
apt-get install build-essential cmake libssh2-1-dev libgcrypt11-dev
- Install Centreon Clib
See the Centreon Clib @TODO@:ref:documentation <centreon-clib:centreon_clib_install>.
In recent OpenSUSE versions, necessary software is available as binary packages from OpenSUSE repositories. Either use the Package Manager or the zypper tool to install them. You should check packages version when necessary.
Package required to build:
| Software | Package Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C++ compilation environment | gcc gcc-c++ make | Mandatory tools to compile. |
| CMake (>= 2.8) | cmake | Read the build script and prepare sources for compilation. |
| Centreon Clib (>= 1.0) | centreon-clib-devel | Core library used by Centreon Connector. |
| ssh2 library | libssh2-devel | SSH library. |
| gcrypt library | libgcrypt-devel | Gcrypt library. |
- Install compilation tools
zypper install gcc gcc-c++ make cmake libssh2-devel libgcrypt-devel
- Install Centreon Clib
See the Centreon Clib @TODO@:ref:documentation <centreon-clib:centreon_clib_install>.
Build
Get sources
Centreon SSH Connector can be checked out from GitHub. The SSH connector sources reside in the ssh subdirectory. On a Linux box with git installed this is just a matter of:
git clone https://github.com/centreon/centreon-connectors
Configuration
At the root of the project directory you'll find a ssh/build directory which holds build scripts. Generate the Makefile by running the following command:
cd /path_to_centreon_connector/ssh/build
Your Centreon SSH Connector can be tweaked to your particular needs using CMake's variable system. Variables can be set like this:
cmake -D<variable1>=<value1> [-D<variable2>=<value2>] .
Here's the list of variables available and their description:
| Variable | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| WITH_CENTREON_CLIB_INCLUDE_DIR | Set the directory path of centreon-clib include. | auto detection |
| WITH_CENTREON_CLIB_LIBRARIES | Set the centreon-clib library to use. | auto detection |
| WITH_CENTREON_CLIB_LIBRARY_DIR | Set the centreon-clib library directory (don't use it if you use WITH_CENTREON_CLIB_LIBRARIES) | auto detection |
| WITH_KNOWN_HOSTS_CHECK | Enable or disable Check hosts against user's known_hosts file. | OFF |
| WITH_LIBGCRYPT_INCLUDE_DIR | Set the directory path of libgcrypt include. | auto detection |
| WITH_LIBGCRYPT_LIBRARIES | Set the libgcrypt library to use. | auto detection |
| WITH_LIBGCRYPT_LIBRARY_DIR | Set the libgcrypt library directory (don't use it if you use WITH_LIBGCRYPT_LIBRARIES) | auto detection |
| WITH_LIBSSH2_INCLUDE_DIR | Set the directory path of libssh2 include. | auto detection |
| WITH_LIBSSH2_LIBRARIES | Set the libssh2 library to use. | auto detection |
| WITH_LIBSSH2_LIBRARY_DIR | Set the libssh2 library directory (don't use it if you use WITH_LIBSSH2_LIBRARIES) | auto detection |
| WITH_PREFIX | Base directory for Centreon SSH Connector installation. If other prefixes are expressed as relative paths, they are relative to this path. | /usr/local |
| WITH_PREFIX_BINARY | Define specific directory for Centreon Connector SSH binary. | ${WITH_PREFIX}/bin |
| WITH_TESTING | Enable generation of unit tests. They can later be run by typing make test. OFF |
Example
cmake \
-DWITH_PREFIX=/usr \
-DWITH_PREFIX_BINARY=/usr/lib/centreon-connector \
-DWITH_TESTING=0 .
At this step, the software will check for existence and usability of the rerequisites. If one cannot be found, an appropriate error message will be printed. Otherwise an installation summary will be printed.
If you need to change the options you used to compile your software, you might want to remove the CMakeCache.txt file that is in the build directory. This will remove cache entries that might have been computed during the last configuration step.
Compilation
Once properly configured, the compilation process is really simple:
make
And wait until compilation completes.
Install
Once compiled, the following command must be run as privileged user to finish installation:
make install
And wait for its completion.
Configuration
Centreon SSH Connector itself does not require any configuration. It should only be configured as a connector of Centreon Engine.
To execute SSH check over SSH with Centreon SSH Connector from Centreon Engine, one might configure commands that relates to SSH check (like check_by_ssh).
Binary arguments
Here are the supported arguments for centreon_connector_ssh:
| Short name | Long name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -d | --debug | If this flag is specified, print all logs messages. |
| -h | --help | Print help and exit. |
| -v | --version | Print software version and exit. |
| -l | --log-file | Specifies the log file (default: stderr). |
| -2 | --proto2 | Tell ssh to use Protocol 2. |
| -4 | --use-ipv4 | Enable IPv4 connection. |
| -6 | --use-ipv6 | Enable IPv6 connection. |
| -a | --authentication | Authentication password. |
| -C | --command | Command to execute on the remote machine. |
| -E | --skip-stderr | Ignore all or first n lines on STDERR. |
| -H | --hostname | Host name, IP Address. |
| -i | --identity | Identity of an authorized key. |
| -l | --logname | SSH user name on remote host. |
| -p | --port | Port number (default: 22) |
| -S | --skip-stdout | Ignore all or first n lines on STDOUT. |
| -t | --timeout | Seconds before connection times out (default: 10). |
Check arguments
These arguments are checks options (like check_by_ssh options).
| Short name | Long name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -1 | --proto1 | This option is not supported. |
| -2 | --proto2 | Tell ssh to use Protocol 2. |
| -4 | --use-ipv4 | Enable IPv4 connection. |
| -6 | --use-ipv6 | Enable IPv6 connection. |
| -a | --authentication | Authentication password. |
| -C | --command | Command to execute on the remote machine. |
| -E | --skip-stderr | Ignore all or first n lines on STDERR. |
| -f | --fork | This option is not supported. |
| -h | --help | Not used. |
| -H | --hostname | Host name, IP Address. |
| -i | --identity | Identity of an authorized key. |
| -l | --logname | SSH user name on remote host. |
| -n | --name | This option is not supported. |
| -o | --ssh-option | This option is not supported. |
| -O | --output | This option is not supported. |
| -p | --port | Port number (default 22). |
| -q | --quiet | Not used. |
| -s | --services | This option is not supported. |
| -S | --skip-stdout | Ignore all or first n lines on STDOUT. |
| -t | --timeout | Seconds before connection times out (default 10). |
| -v | --verbose | Not used. |
| -V | --version | Not used. |
Example:
define connector{
connector_name centreon_connector_ssh
connector_line /usr/lib64/centreon-connector/centreon_connector_ssh --log-file=/var/log/centreon-engine/centreon-connector-ssh.log
}
define command{
command_name ssh_check_cpu
command_line $USER1$/check_by_ssh -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -l $_HOSTUSER$ -a $_HOSTPASSWORD$ -C "$USER1$/check_cpu -w $ARG1$ -c $ARG2$"
connector centreon_connector_ssh
}
define command{
command_name ssh_check_disk
command_line $USER1$/check_by_ssh -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -l $_HOSTUSER$ -a $_HOSTPASSWORD$ -C "$USER1$/check_disk -D $ARG1$ -w $ARG2$ -c $ARG3$"
connector centreon_connector_ssh
}
Technical details
This article describes how Centreon SSH Connector allow much gain on SSH check execution.
One major CPU-intensive and long operation in a SSH environment is the key exchange and verification mechanism. This operation occurs when a SSH session is started between two hosts. After this step all exchange operations are using far less resources.
Centreon SSH Connector take advantage of this fact and maintain semi-permanent connection with hosts to which it had to connect to. This way if multiple checks are performed on the same host, where "check_by_ssh" opens one session for each check, Centreon Connector SSH only opens one session. However this does not limit the number of concurrent checks on a host, as the SSH protocol allows multiple channels to be opened on the same session. Therefore if multiple checks are run on the same host simultaneously, they are executed concurrently but with separate execution environment.
Perl connector
Centreon Perl Connector is a free software from Centreon available under the Apache Software License version 2 (ASL 2.0). It speeds up execution of Perl scripts when used along Centreon Engine.
Installation
Centreon recommends using its official packages. Most of Centreon’ endorsed software are available as RPM packages.
Run the following commands as privileged user:
yum install centreon-connector-perl
Or you can build the Centreon SSH Connector. You will need the following external dependencies:
- a C++ compilation environment.
- CMake (>= 2.8), a cross-platform build system.
- Centreon Clib, The centreon Core library.
- ssh2 library to use ssh functions.
- gcrypt library to secure connections.
This program is compatible only with Unix-like platforms (Linux, FreeBSD, Solaris, ...).
Prerequisites
- CentOS
- Debian/Ubuntu
- OpenSUSE
In CentOS you need to add manually cmake. After that you can install binary packages. Either use the Package Manager or the yum tool to install them. You should check packages version when necessary.
Package required to build:
| Software | Package Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C++ compilation environment | gcc gcc-c++ make | Mandatory tools to compile. |
| CMake (>= 2.8) | cmake | Read the build script and prepare sources for compilation. |
| Centreon Clib (>= 1.0) | centreon-clib-devel | Core library used by Centreon Connector. |
| Perl | perl | Scripting language. |
- Install basic compilation tools
yum install gcc gcc-c++ make perl
- Install cmake
yum install cmake
- Install Centreon Clib
See the Centreon Clib @TODO@:ref:documentation <centreon-clib:centreon_clib_install>.
In recent Debian/Ubuntu versions, necessary software is available as binary packages from distribution repositories. Either use the Package Manager or the apt-get tool to install them. You should check packages version when necessary.
Package required to build:
| Software | Package Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C++ compilation environment | build-essential | Mandatory tools to compile. |
| CMake (>= 2.8) | cmake | Read the build script and prepare sources for compilation. |
| Centreon Clib (>= 1.0) | centreon-clib-devel | Core library used by Centreon Connector. |
| Perl | libperl-dev | Scripting language. |
- Install compilation tools
apt-get install build-essential cmake libperl-dev
- Install Centreon Clib
See the Centreon Clib @TODO@:ref:documentation <centreon-clib:centreon_clib_install>.
In recent OpenSUSE versions, necessary software is available as binary packages from OpenSUSE repositories. Either use the Package Manager or the zypper tool to install them. You should check packages version when necessary.
Package required to build:
| Software | Package Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C++ compilation environment | gcc gcc-c++ make | Mandatory tools to compile. |
| CMake (>= 2.8) | cmake | Read the build script and prepare sources for compilation. |
| Centreon Clib (>= 1.0) | centreon-clib-devel | Core library used by Centreon Connector. |
| Perl | perl | Scripting language. |
- Install compilation tools
zypper install gcc gcc-c++ make cmake perl
- Install Centreon Clib
See the Centreon Clib @TODO@:ref:documentation <centreon-clib:centreon_clib_install>.
Build
Get sources
Centreon Perl Connector can be checked out from GitHub. The Perl connector sources reside in the perl subdirectory. On a Linux box with git installed this is just a matter of:
git clone https://github.com/centreon/centreon-connectors
Configuration
At the root of the project directory you'll find a perl/build directory which holds build scripts. Generate the Makefile by running the following command:
cd /path_to_centreon_connector/perl/build
Your Centreon Perl Connector can be tweaked to your particular needs using CMake's variable system. Variables can be set like this:
cmake -D<variable1>=<value1> [-D<variable2>=<value2>] .
Here's the list of variables available and their description:
| Variable | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| WITH_CENTREON_CLIB_INCLUDE_DIR | Set the directory path of centreon-clib include. | auto detection |
| WITH_CENTREON_CLIB_LIBRARIES | Set the centreon-clib library to use. | auto detection |
| WITH_CENTREON_CLIB_LIBRARY_DIR | Set the centreon-clib library directory (don't use it if you use WITH_CENTREON_CLIB_LIBRARIES) | auto detection |
| WITH_PREFIX | Base directory for Centreon PErl Connector installation. If other prefixes are expressed as relative paths, they are relative to this path. | /usr/local |
| WITH_PREFIX_BINARY | Define specific directory for Centreon Connector Perl binary. | ${WITH_PREFIX}/bin |
| WITH_TESTING | Enable generation of unit tests. They can later be run by typing make test. | OFF |
Example
cmake \
-DWITH_PREFIX=/usr \
-DWITH_PREFIX_BINARY=/usr/lib/centreon-connector \
-DWITH_TESTING=0 .
At this step, the software will check for existence and usability of the rerequisites. If one cannot be found, an appropriate error message will be printed. Otherwise an installation summary will be printed.
If you need to change the options you used to compile your software, you might want to remove the CMakeCache.txt file that is in the build directory. This will remove cache entries that might have been computed during the last configuration step.
Compilation
Once properly configured, the compilation process is really simple:
make
And wait until compilation completes.
Install
Once compiled, the following command must be run as privileged user to finish installation:
make install
And wait for its completion.
Configuration
Centreon Perl Connector itself does not require any configuration. It should only be configured as a connector of Centreon Engine.
To execute Perl scripts with Centreon Perl Connector from Centreon Engine, one might configure commands that relates to Perl scripts. Such commands must only contain the path to the Perl script to execute followed by its arguments, just like one would on the command line. To make it simple, you just have to add a connector property to your command definition.
Binary arguments
Here are the supported arguments for centreon_connector_perl:
| Short name | Long name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -d | --debug | If this flag is specified, print all logs messages. |
| -h | --help | Print help and exit. |
| -v | --version | Print software version and exit. |
| -c | --code | Argument is some Perl code that will be executed by the embedded interpreter. |
| -l | --log-file | Specifies the log file (default: stderr). |
Example:
define connector{
connector_name centreon_connector_perl
connector_line /usr/lib64/centreon-connector/centreon_connector_perl --log-file=/var/log/centreon-engine/centreon-connector-perl.log
}
define command{
command_name check_ping
command_line $USER1$/check_ping.pl -H $HOSTADDRESS$
connector centreon_connector_perl
}
define command{
command_name check_disk
command_line $USER1$/check_disk.pl -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -D $ARG1$
connector centreon_connector_perl
}
Technical details
This article describes how Centreon Perl Connector allow much gain on Perl script execution.
First of all let's examine how a Perl script is executed traditionnally by Centreon Engine.
- Centreon Engine forks, creating a new separate process.
- This new process executes the execve syscall to run the Perl interpreter. This step does not create a new process.
- The Perl interpreter parse the Perl script.
- Perl script get executed.
With Centreon Engine, the same script get executed multiple times but with different arguments. Therefore we took advantage of this fact to efficiently parse all the scripts once and get them executed. This was only possible because of the fork()ing system of Unix-like platform. If you read the reference page on Wikipedia you indeed remarked that once fork()ed the old and the new process are identical. Centreon Connector Perl's steps to execute scripts are as follow.
- Centreon Engine creates a resident process of Centreon Connector Perl once
- For all Perl scripts execution requests are forwarded to this process when requested to execute a script, Centreon Perl Connector checks if this script has already been parsed if not it parses it using the Embedded Perl interpreter.
- Centreon Perl Connector forks itself.
- The precompiled script gets executed
This way Perl scripts are only parsed once during the lifetime of the monitoring engine. This heavily relates to prepared statements in SQL.