Debug SNMP Traps management
Debug SNMP Traps
Several elements are involved in the SNMP traps management. In case of problem, it is necessary to check the proper functioning of its architecture, there are several things to check.
Sender settings
The first point is to control the configuration of the equipment or application that issued the trap that you should have received. Check IP address or DNS name, the SNMP community and version.
Firewall, routing
The second point is to control network firewalls and software permissions and the implementation of a specific routing. If one or more network firewalls are present or if a port translation and/or IP address is in place, make sure the connection is possible between the emitter and the poller. The use of network probes, debug network devices (firewalls and routers) or software tcpdump/wireshark on the poller may help you to confirm receipt of data on UDP port 162.
Snmptrapd
After validation of the connection, check the operating status of snmptrapd process (which must be running) and its configuration options. It is possible to enable logging of the process. To do this change the /etc/sysconfig/snmptrapd file and replace the "OPTIONS" line:
# snmptrapd command line options
# OPTIONS="-On -d -t -n -p /var/run/snmptrapd.pid"
OPTIONS="-On -Lf /var/log/snmptrapd.log -p /var/run/snmptrapd.pid"
Restart the process to take the changes into account. Thus, for any receiving SNMP traps, these events will be listed in the /var/log/snmptrapd.log log.
In case you filter by SNMP community, check allowed communities in the configuration file /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf. If after all these checks, SNMP traps are not included in the log, verify that the process is listening on UDP port 162 for remote equipment using the command:
netstat -ano | grep 162
You must have a result like:
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:162 0.0.0.0:* off (0.00/0/0)
If not, change the listening port of the process.
Don't forget to deactivate the logs after your check. Otherwise, the volume of the logs can be very important.
Centreontrapdforward
Once the snmptrapd process is validated, check the centreontrapdforward process. The first step is to check the access parameters of this process snmptrapd in the file /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf
- Check that snmptrapd service executes centreontrapdforward. To do this, edit the file /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf and verify that its contains:
traphandle default su -l centreon -c "/usr/share/centreon/bin/centreontrapdforward"
If path to the file is incorrect, change it and restart the snmptrapd process. You can check the proper functioning of binary centreontrapdforward by checking the configuration part of centreontrapdforward.
Centreontrapd
The next process to check is Centreontrapd. This daemon allows to connect a SNMP trap to a passive service linked to an host in Centreon using IP address or DNS from distant equipment. To check its operation, you should check the centreontrapd configuration settings.
You can check the proper functioning of binary centreontrapd by checking the configuration part of centreontrapd.
You can set up debug mode for the centreontrapd service. Edit the following file:
vi /etc/sysconfig/centreontrapd
Then modify option severity to debug:
OPTIONS="--logfile=/var/log/centreon/centreontrapd.log --severity=debug --config=/etc/centreon/conf.pm --config-extra=/etc/centreon/centreontrapd.pm"
Then restart centreontrapd:
systemctl restart centreontrapd
Centreon Gorgone
Gorgoned daemon must be running to forward information from Centreontrapd to the monitoring engine as an external command. Enable the debug mode via Administration > Parameters > Debug menu and restart process.
You can change logging level through Administration > Parameters > Debug menu.
If any external command are sent to the monitoring engine please check the path to "$cmdFile"" in /etc/centreon/conf.pm configuration file. The path should be /var/lib/centreon/centcore.cmd for a central Centreon server.
Centreon Engine
The monitoring engine must receive external commands from Centreon Gorgone process in order to change status and output of the passive service. Please check the event log. For Centreon Engine, the path is /var/log/centreon-engine/centengine.log. You should find lines as:
[1352838428] EXTERNAL COMMAND: PROCESS_SERVICE_CHECK_RESULT;Centreon-Server;Traps-SNMP;2;Critical problem
[1352838433] PASSIVE SERVICE CHECK: Centreon-Server;Traps-SNMP;2;Critical problem
If only the external command appears but not the consideration thereof by the scheduler ("PASSIVE SERVICE CHECK"), there may be a system clock problem synchronizing issue. The server is late and the order will be processed later, either in advance and the order will not be taken into account.
Centreon UI
To display the result in Centreon the monitoring engine must forward using NEB module information to the broker to store them into database. Centreon will display result from "centreon_storage" database. If you can reach Centreon web interface you must see the change of the output and maybe the status of the passive service. If any change appears a connection failure between the monitoring engine and the broker can be the root cause of this issue. Problems can be:
- The monitoring engine doesn't load the NEB module to connect to the distant broker.
- The NEB module settings are wrong to connect to the distant broker.
- A firewall stops the connection.
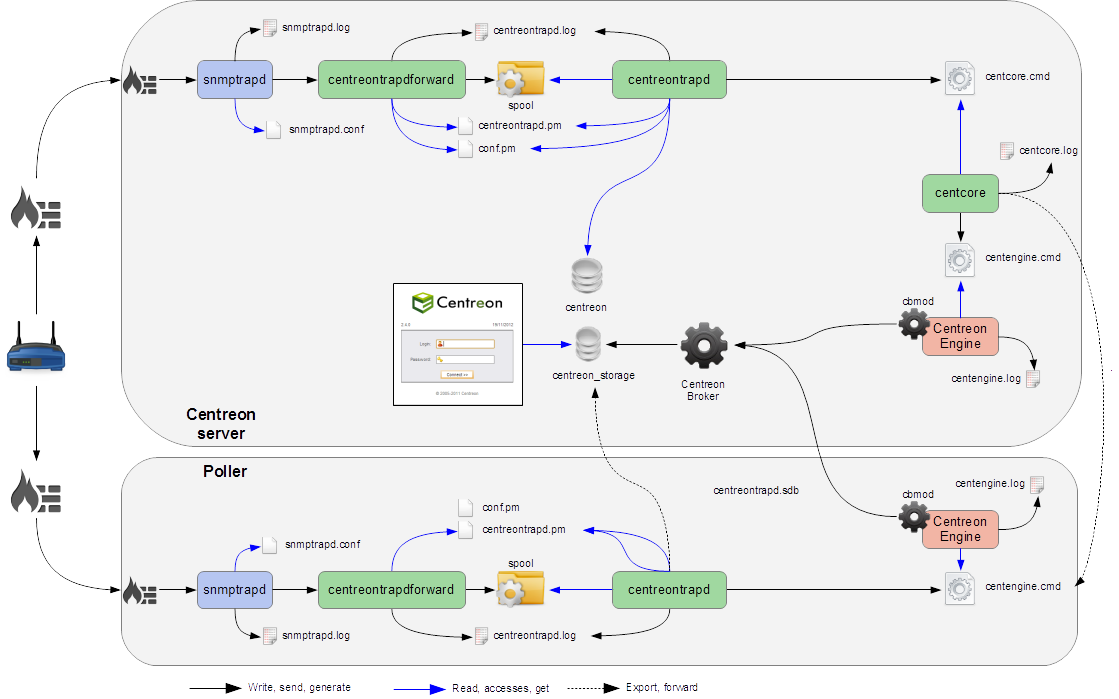
Detailed diagram
You will find below a detailed diagram of all the processes used and/or present at the reception of an SNMP trap: