Configuring notifications
Prerequisites
Step 1: Check that the monitoring engine is programmed to send notifications.
-
Go to Configuration > Pollers > Engine configuration.
-
Click on the poller you want.
-
On the Check Options tab, in the Misc options section, select Yes for the Notification Option option.
-
Click Save.
Step 2: Check that your Centreon can send notifications, e.g. emails.
Notification commands are executed by the poller that monitors the resource: you will need to configure the ability to send notifications on all pollers.
Configuring notifications
Step 1: Defining when checks must be made
-
Go to Configuration > Hosts > Hosts or Configuration > Services > Services by host and select a host or service.
-
On the General Information tab, fill in section Host/Service Scheduling Options. If no values are defined on the host or service, the host or service will inherit the values from its parent template (see Template inheritance rules).
| Action | Option to fill in |
|---|---|
| Enable active checks. | Set Active checks enabled to Yes |
| Define during which time period active checks should be made. Outside this time period, no checks will be made, which means that no notifications will be sent. | Check Period |
| Define how often active checks should be made when the host is in an OK state. | Normal Check Interval |
Define what happens when the host or service enters a non-UP or non-OK (SOFT) state:
|
|
| When the host or service enters a HARD state, notifications start being sent. | The host is checked at the Normal check interval, and a notification can only be sent when a check has been made |
Step 2: Configuring the notifications on the host or service
To make the configuration of notifications faster, you can define the parameters on a host/service template. All hosts or services that inherit this template will also inherit these settings. See Template inheritance rules.
-
Go to Configuration > Hosts > Hosts or Configuration > Hosts > Services and select a host or service.
-
On the Notifications tab:
-
Make sure Notifications Enabled is set to Yes.
If it is set to Default, the value applied will be that defined on the host or service template (see Template Inheritance Rules). If no value is defined on any parent template, the default value is No.
-
In Linked Contacts/Linked Contact Groups, define which contacts will receive notifications. Notifications must be enabled for these contacts (see Step 3).
If notifications are enabled for a host and a contact is defined, notifications will also be enabled for the host's services (unless their notification Enabled option is set to No).
-
Notification options: Define for which statuses notifications must be sent. If no value is defined here, the value will be inherited from a parent template (see Template inheritance rules). If no value is defined on any parent template, notifications will be sent for all statuses except for None.
-
Notification Interval: Define the number of “time units” to wait before re-notifying a contact that this host is still not up/that this service is still in a not-OK condition.
- With the default time unit of 60s, this number will mean multiples of 1 minute.
- Enter 0 to send just 1 notification.
- Be aware that a notification can only be sent if a check has occurred. In order to get the expected results, the value defined in this field must be a multiple of the Normal Check Interval option defined on the General Information tab.
- If no value is defined here, the value will be inherited from a parent template (see Template inheritance rules).
- If nothing is defined on the host/service or on any of its parent templates, the default value is 30 minutes.
-
Notification period: Specify the time period during which notifications of events for this host or service can be sent out to contacts.
- If a state change occurs during a time which is not covered by the time period, no notifications will be sent out.
- If no value is defined on the host/service or any of its parent templates, the default value is 24x7.
-
First notification delay: Define the number of “time units” to wait before sending out the first problem notification when the host enters a HARD non-UP state/when the service enters a HARD non-OK state. The host or service enters a HARD state after the Max check attempts has been reached (defined on the General Information tab)
- With the default time unit of 60s, this number will mean multiples of 1 minute.
- If you set this value to 0, the monitoring engine will start sending out notifications immediately.
- If nothing is defined on the host/service or on any of its parent templates, the default value is 0.
-
Recovery notification delay: Define the number of “time units” to wait before sending out the recovery notification when this host enters an UP state/when this service enters an OK state.
- With the default time unit of 60s, this number will mean multiples of 1 minute.
- If you set this value to 0, monitoring engine will start sending out notifications immediately.
- If nothing is defined on the host/service or on any of its parent templates, the default value is 0.
-
-
Deploy the configuration.
Step 3: Enabling notifications for the contacts you have defined
To make the configuration of notifications faster, you can define the parameters on a contact template. All contacts that inherit this template will also inherit these settings. See Template inheritance rules.
-
Go to Configuration > Users > Contacts/Users and then click on the contact you want to be notified.
-
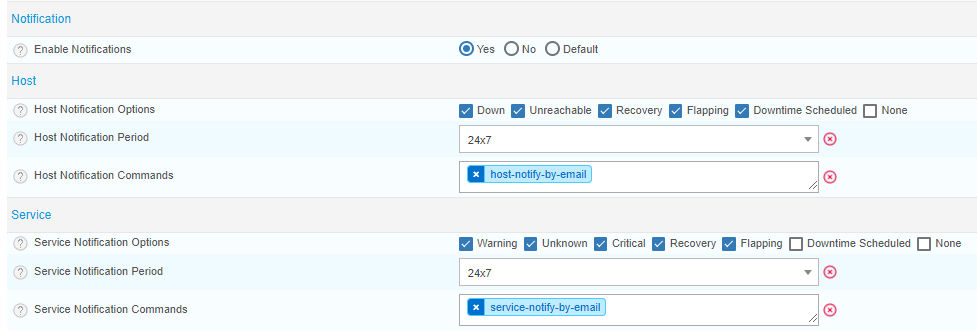
On the General Information tab, in section Notification, check that Enable notifications is set to Yes.
If the option is set to Default, Centreon will use the value defined on the closest parent template. If no value is defined on any parent template, Default means No unless the contact has been configured to be notified on a host.
-
In sections Host and Service, check that the options are consistent with what you have defined at host/service level:
- For instance, if you have set the Host Notification Options to None on the contact, the contact will receive no notifications for the host, even if you have enabled all types of notifications for the host. If you have enabled all types of notifications on the contact but only Critical notifications on a service, the contact will only receive Critical notifications for this service.
- If you have defined no rule on the contact, the rules defined in the closest contact template are applied.
- If you have defined rules on the contact, these will take precedence over rules defined on the contact template.
-
Click Save.
-
Deploy the configuration.
Reference
-
Host/Service Notification Options: define in which cases the contact must receive a notification. If you select None, the contact will receive no notifications of any kind for hosts or services.
-
Host/Service notification Period: define during which time period the contact will receive notifications. If a state change occurs during a time which is not covered by the time period, no notifications will be sent out (even if the time period matches that defined for the host or service). Bear in mind that this time period will match the timezone defined in the user's profile (i.e. if the time period is 9 to 5 pm, the user will receive notifications between 9 and 5 pm in his timezone, which is not necessarily the same as yours).
-
Host/Service notification Commands: define how the contact should be notified (email, pager, jabber).
Checking the configuration of notifications
You can quickly check whether the configuration is well applied in the Resources Status page.
-
Go to Monitoring > Resources Status.
-
Click on the resource that you have configured notifications for. A detail panel opens on the right side.
-
Click on the Notification tab.
This tab shows whether notifications are enabled for this resource, and lists the contacts and contact groups that will be notified.
Template inheritance rules
For hosts and services, section Scheduling Options/Service Scheduling Options of the General information tab, and section Notification Options of the Notifications tab, work in the same way.
- If you fill in the options on the host or service, the values will override any value set in the templates for the host or service.
- If no values are defined here, what will be applied are the values defined in the host's or service's template, or in their parent template, or in the parent of the parent template, etc. What takes precedence is always what is defined on the object itself or closest to it.
Example :
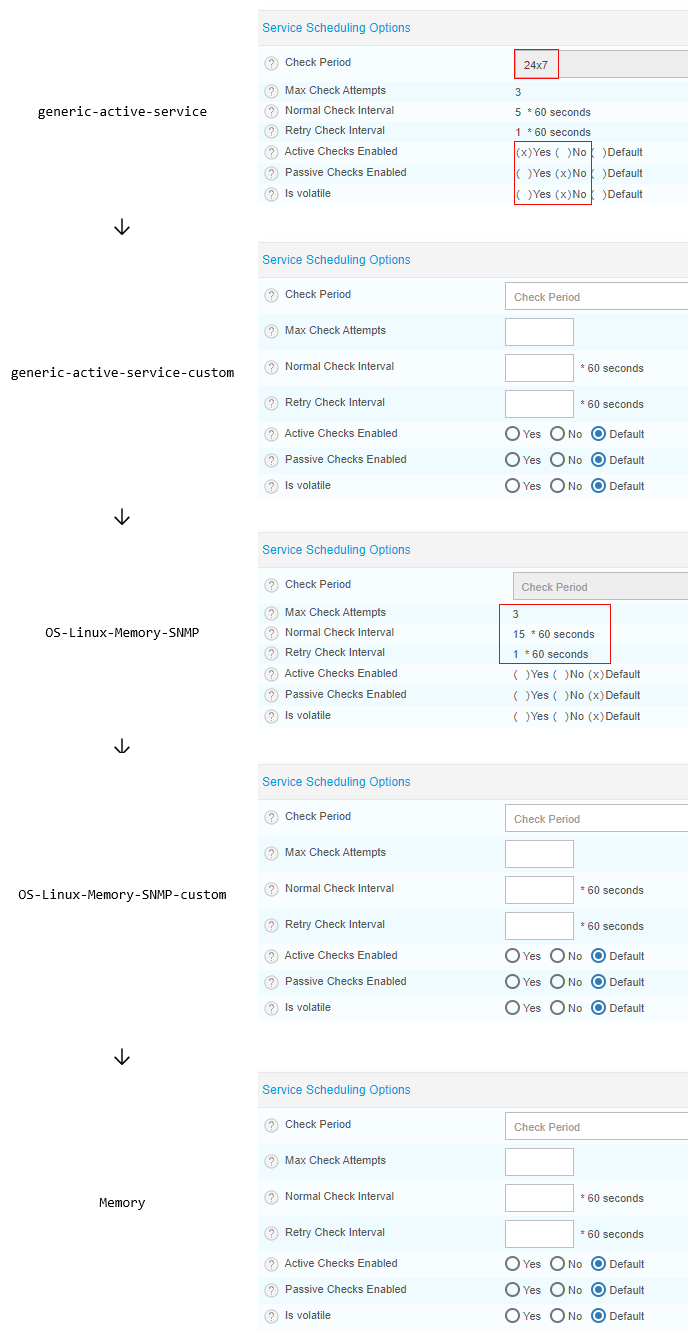
A service called Memory has the following parent templates: Memory < OS-Linux-Memory-SNMP-custom < OS-Linux-Memory-SNMP < generic-active-service-custom < generic-active-service.
- Memory has nothing defined in Service Scheduling Options.
- Its grandparent template, OS-Linux-Memory-SNMP, has values defined for Max check attempts, Normal Check Interval and Retry Check Interval: these will be applied to Memory.
- However, OS-Linux-Memory-SNMP has no values defined for Check period, Active Checks Enabled, Passive Checks Enabled and Is volatile. So we need to go up two levels: these values are defined on the template called generic-active-service.
Contacts & Contact groups method calculation
Since Centreon version 19.10, 3 methods for determining the contacts and groups of contacts that will be notified are available. These are defined on page Administration > Parameters > Centreon UI:
- Vertical Inheritance Only: get contacts and contactgroups of resources and linked templates, using additive inheritance enabled option (Legacy method, keep for upgrade)
- Closest Value: get most closed contacts and contactgroups of resources including templates
- Cumulative inheritance: Cumulate all contacts and contactgroups of resources and linked templates (method used for new installation)
The Cumulative inheritance option is the easiest to program.
Troubleshooting
Contacts are not receiving notification emails
Check the following points:
-
Is the postfix service running? Use the following command:
systemctl status postfix -
Is the following file configured correctly?
/etc/postfix/main.cf -
Are notifications enabled for the contact? Are notifications configured correctly on the contact?
-
Are notifications configured correctly on the host or service?
Notifications are not sent in the specified interval
Check that the value you have defined in Notification Interval (on the 2nd tab) is a multiple of the value defined in Normal Check Interval (on the 1st tab).
Indeed, a notification can only be sent if a check has occurred. If you decide that checks happen every hour but notifications are to be sent out every 10 minutes, the notifications will actually be sent every hour because checks only happen every hour and not every 10 minutes.
Notifications have been sent outside the user's time period
Check the user's timezone:
- Go to Configuration > Users > Contacts/Users and then click on the contact you want to be notified.
- Check the Timezone/Location field. The time period during which notifications will be sent to a user is the time period in his timezone.